The initial management of someone who has just been diagnosed as having diabetes mellitus can have a big effect on the course of the illness. It is essential to establish a clear understanding of the disease, the benefits of all aspects of management.
Diabetes management should be discussed with the patient and initiated as soon as possible. Advice on diet and exercise recommendations for people with diabetes.
Life style Management
Eat Healthy: Healthy eating is a critical part of managing your diabetes allowing blood sugar to reach target levels and prevent from diabetes complications.
You can control your blood sugar if you:
- Maintain an optimal weight
- Pay attention to what and how much you eat.
A healthy diet is a diet that provides the nutrients to your body needs in sufficient amounts.
Ensure a healthy meal plan: A diabetes meal plan is a guide that tells you how mush and what kind of food you can choose to eat at meal and snack
- Eat variety of foods to ensure a balanced diet.
- Eat plenty of vegetables and fruits.
- Ensure moderate use of edible oils and animal foods and very less use of ghee, butter and vanaspati.
- Overeating should be avoided to prevent weight gain.
- Exercise regularly and be physically active.
- Use salt in moderation
- Practice right cooking methods to maintain the nutritious value of foods, drink plenty of water.
- Minimize the use of processed foods rich in salt, sugar and fats
- Include micronutrient-rich foods in diet.
Use the diabetes food pyramid:
Divide food into groups based on what they contain. Eat more from groups at the bottom of pyramid and less from groups at the top.

Main pillar in prevention of Diabetes
- Improves psychological well-being
- Changing habits is difficult
- Set realistic goals to achieve
- Increase daily physical activity – any activity is useful, having fun
- important factor in keeping active
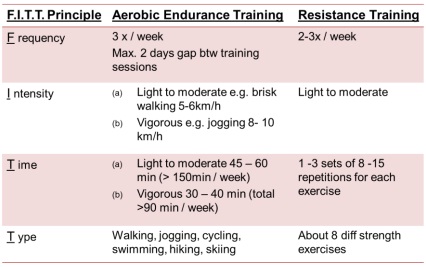
People with diabetes should be advised to perform at least 150 min/week of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity (50–70% of maximum heart rate) and if no contraindications, resistance training three times per week should be encouraged.
Progressive resistance exercise improves insulin sensitivity in older men with type 2 diabetes to the same or even a greater extent as aerobic exercise.