We often hear people say “sugar hai”. What it means is that the person has high blood sugar levels and is suffering from the disease known as diabetes. Diabetes is the condition where a person’s body does not produce sufficient insulin to process the carbohydrates and fats produced by the food partaken and accumulated in the blood. Either the insulin production is reduced or the food ingested needs much more insulin than normal.
Type 1 diabetes is generally a hereditary condition and can manifest from birth but generally, symptoms appear from age twelve. Type 2 diabetes is more of a lifestyle disease. Meaning, that the lifestyle of a person affects his/her health- like diet, lack of exercise, stress, lack of sleep or an unhealthy everyday routine. Even pregnant women can have temporary diabetes during pregnancy known as Gestational diabetes.
Glycaemia : ‘Glyco’ means sugar and ’emia’ means a condition of the blood. So, technically glycaemia means the presence of sugar or glucose in the blood. Some foods cause high blood sugar levels where sugar levels shoot up very fast. This happens because carbohydrates like refined sugars and bread are easily converted into glucose which is the sugar that is converted for energy. Carbs from vegetables and whole grains take longer to digest and slower release of sugars/glucose.
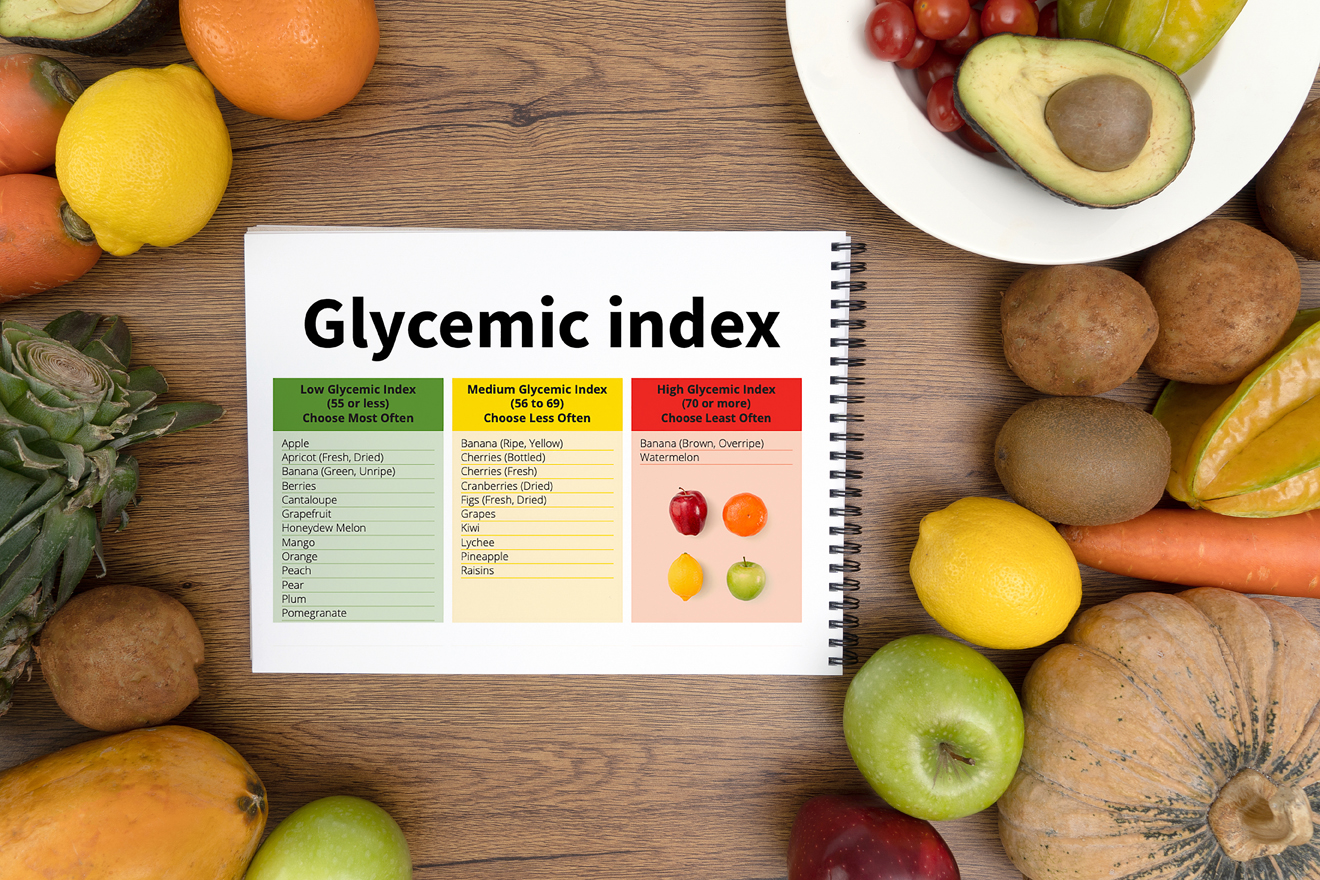
Glycemic Index : The glycemic index is a scale that computes the number of carbohydrates in foods and indicates how quickly that particular food causes a spike or a high in the person’s blood sugar. The lower the GI (glycaemic Index) the better for diabetics or people on a weight loss programme.
- GI of under 55 (low) is the best
- GI of 56-69 (medium)
- GI of 70 or higher (high) bad
For a person suffering from diabetes, a strict regimen of diet and exercise is necessary to keep blood sugar levels under control. Exercise burns the sugars and diet regulates the production of sugars.
It is important to be on a diet which has foods that are low on the Glycaemic Index.
- Cooking tends to raise the Glycemic Index of the food: Pasta will have a lower GI if it is firm and not overcooked than it will if it is cooked very soft.
- Processing raises the Glycemic Index. Fruit juice typically has a higher GI than whole fruit.
- Riper foods usually have a higher Glycemic Index. The GI of a banana will get higher as the banana ripens.
- Eating fibre is very good as it lowers the GI of that food
Foods and their GI :
| Fruits | |
| Apples (120g) | 40 |
| Apricots, dried (60g) | 32 |
| Bananas (120g) | 47 |
| Grapefruit (120g) | 25 |
| Grapes (120g) | 43 |
| Mangoes (120g) | 51 |
| Oranges, raw (120g) | 48 |
| Pineapple (120g) | 51 |
| Plums (120g) | 53 |
| Strawberries (120g) | 40 |
| Vegetables | |
| Carrots, raw (80g) | 35 |
| Corn, sweet (80g) | 55 |
| Potato, white, boiled (150g) | 54 |
| Tomato soup (250 g) | 38 |
| Grains, Breads & Cereals | |
| Barley (150g) | 22 |
| Basmati rice (150g) | 52 |
| Bran cereal (30g) | 43 |
| Brown rice, steamed (50g) | 50 |
| Bulgur wheat, whole, cooked (150g) | 46 |
| Chickpeas (150g) | 36 |
| Instant noodles (180g) | 52 |
| Instant oatmeal (25 g) | 50 |
| Mixed grain bread (30g) | 52 |
| Oat bran bread (30g) | 44 |
| Rye kernel bread (30 g) | 41 |
| Rye flour bread, 50% rye flour, 50% wheat flour (30g) | 50 |
| Water crackers, whole grain, sesame seeds (25g) | 53 |
| White rice, boiled (150g) | 47 |
| Dairy and Dairy Alternatives | |
| Skim milk (250g) | 32 |
| Soy milk (250g) | 43 |
| Nuts and Legumes | |
| Black beans (150g) | 30 |
| Butter beans (150g) | 36 |
| Cashews (50g) | 25 |
| Kidney beans (150g) | 29 |
| Kidney beans, canned (150g) | 52 |
| Lentils, canned (150g) | 42 |
| Split peas, yellow, boiled (150g) | 25 |
| Snacks & Sweets | |
| Blueberry muffin (60g) | 50 |
| Cake, pound (50g) | 38 |
| Corn chips (50g) | 42 |
| Hummus (30g) | 6 |
| Ice cream, full-fat, French vanilla (50g) | 38 |
| Ice cream, low-fat, vanilla, “light” (50g) | 46 |
| Oatmeal cookies (25g) | 54 |
| Snickers (60g) | 43 |
| Sponge cake (63g) | 46 |
| Strawberry jam (30g) | 51 |
| Sushi (100g) | 55 |