Diabetes management requires awareness to know what makes your blood sugar level rise and fall – and how to control these day-to-day factors. The plan involves healthy eating , physical activity and medication (insulin and other diabetes medications) designed to lower your blood sugar level when diet and exercise alone aren’t sufficient for managing the condition. Treatment of diabetes primarily involves monitoring of your blood sugar, along with oral diabetes medications, insulin or both. Insulin therapy is an important part of diabetes treatment. Understanding insulin administrating technique can help you manage your diabetes better.
Insulin:
It is a naturally occurring hormone produced by pancreas that regulate your blood glucose levels. In case of diabetes, your body either resists the effects of insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain a normal glucose level. Insulin is required for people with diabetes. The efficacy of injection therapy in diabetes depends on correct injection technique. Good injection technique is vital in achieving glycemic control and thus preventing complications of diabetes
Insulin Injection Technique:
Insulin injection technique is important in order to ensure that proper dose of Insulin is delivered in our body. Flaws in the technique will ultimately affect the glyceamic control. At the beginning of injection therapy, you should discuss the following with your doctor
- Injection Regimen
- Choice and management of device to be used.
- Correct Injection techniques (including site rotation, injection angle and possible use of skin folds)
- Injection complications and how to avoid them
- Safe disposal of used sharps
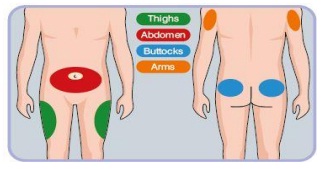
Injection Sites:
- Recommended injection sites for
- injectable therapy.
- Absorption is fastest with injection in
- the abdomen, followed by the arms,
- thighs and buttocks.
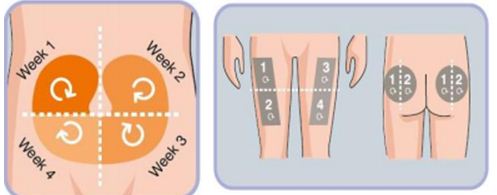
Rotation of Injection Sites:
- Rotation of injection site is critical to prevent lipohypertrophy (a lump under theskin caused by extra fat)
- Lipohypertrophy has been linked to poorer glycemic control and may reduceabsorption by 25%
- Rotation is typically made within the general arm rather than from major site to site.
- Divide the injection site in to quadrants(abdomen) or halves (thighs or buttocks),using one quadrant per week)
- Move always clockwise
- Injection should be atleast 1 cm spaced if done within the same quadrant to avoid repeat tissues trauma.
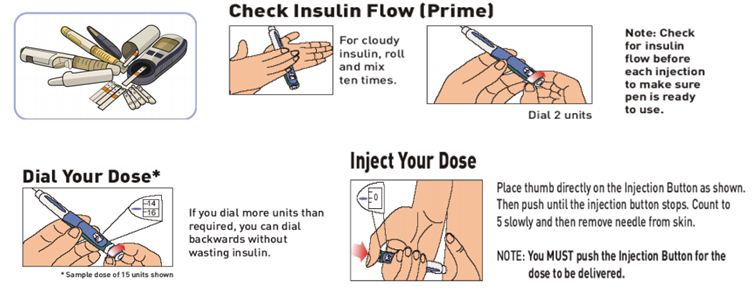
Injecting the dose:
- Choose an injection site.
- Use needles of shorter length and smaller diameter.
- Clean the skin with an alcohol swab. Pinch up a large area of skin.
- Insert the needle into the skin at a90 degrees angle. Make sure the needle is in all the way.
- Push the plunger all the way
- Pull the needle straight out.
- Do not rub the injection site. Safely discard the needle and syringe
How to use pen devices:
Pens come in two basic types:
- Disposable pens are preloaded with insulin and are discarded after the insulin catridge is empty or the pen has been in use for 28 to 32 days.
- Reusable pens work with insulin catridges that can be loaded into the pen and then tossed away once the insulin is used, leaving the pen ready for next cartridge.
Insulin storage:
- Keep insulin away from heat and light. Any Insulin that you don’t store in the refrigerator should be kept as cool as possible.
- Never let your insulin freeze.
Carrying Insulin while travelling:
- Protect insulin from getting too hot and too cold. Don’t leave insulin in a parked car when temperature are extreme.
- When travelling by bus, train or plane, keep your insulin and other medicines, andiabetes supplies with you in an insulated bag.
- To get through airport security, keep your insulin in its original packaging with the prescription label. Have a note from your doctor or pharmacist stating that you are carrying medicine and supplies for diabetes.
Managing GDM at Apollo Sugar :
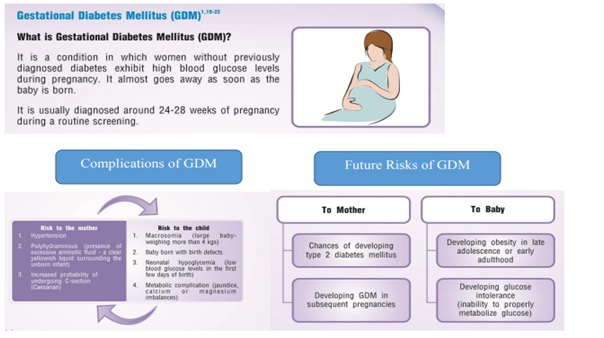
How to manage GDM:
SMBG: In order to maintain set the Blood Glucose Targets by your doctor
Recommended pattern of blood glucose testing for GDM patients: Ideally,4 times a day, fasting and either 1-2 hours post meals
Regular physical activity as recommended by your doctor
Take the medications regularly as per your doctors’ advice
Post-partum follow up : it is generally recommended that all women with GDM be checked after 6 weeks following delivery. Since, they are also at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes in future; practicing lifestyle is warranted.
