Peripheral artery disease refers to the disease of arteries of the legs. This disease is characterized by burning sensation in legs, leg pain (even at rest), numbness in the legs, intermittent claudication, and loss of hair growth in the legs.
Peripheral artery disease manifests in the form of reduced blood supply to the limbs and can lead to gangrene, foot amputation, heart disease, coronary heart disease, heart attack, and stroke.
Diagnosis of peripheral artery disease
As such, peripheral artery disease is caused due to atherosclerosis of the arteries in the legs. Atherosclerosis is the formation of plaques in the arteries leading to obstruction of blood vessels. As oxygenated blood is deprived to the tissues, there is damage to the tissues.
When there is damage to the tissue of the legs due to obstruction of blood flow, people experience symptoms of peripheral artery disease. Once a person experiences symptoms of peripheral artery disease, doctors prescribe certain diagnostic tests in order to confirm the diagnosis of peripheral artery disease.
Tests done to diagnose peripheral artery disease
After taking a detailed physical examination and a past medical history, doctors order certain investigative tests to confirm the diagnosis of peripheral artery disease.
Physical examination
If the patient has:
- No distal pulse (pulse at the ankle)
- Cool skin
- Non-healing wounds
- Shiny skin
- Absence of hair on the legs
Upon presence of the above signs, doctors generally order further investigations. These include:
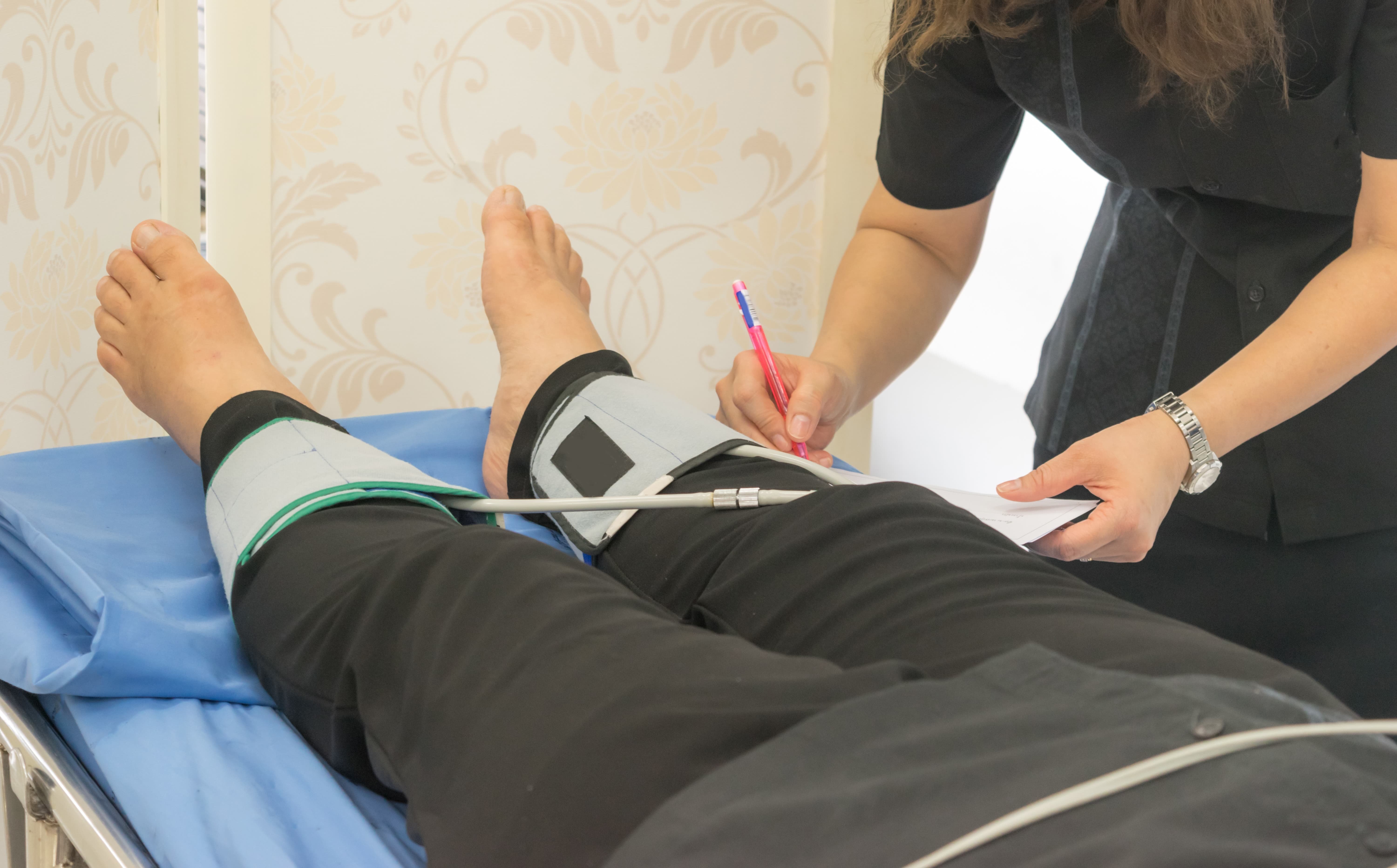
Ankle-Brachial index
Ankle-brachial index is a ratio of blood pressure. This test is done by measuring blood pressure at the ankle and the upper arm. This is a reliable and inexpensive test in order to diagnose peripheral artery disease. People with an ankle-brachial index of 0.90 or less are diagnosed with peripheral artery disease.
This test is advised to people above the age of 50 years with diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol levels irrespective of the fact that they have peripheral artery disease or not.
Other diagnostic tests include:
- CT-angiography
- MRI
- Angiography with contrast
- Doppler Ultrasonography