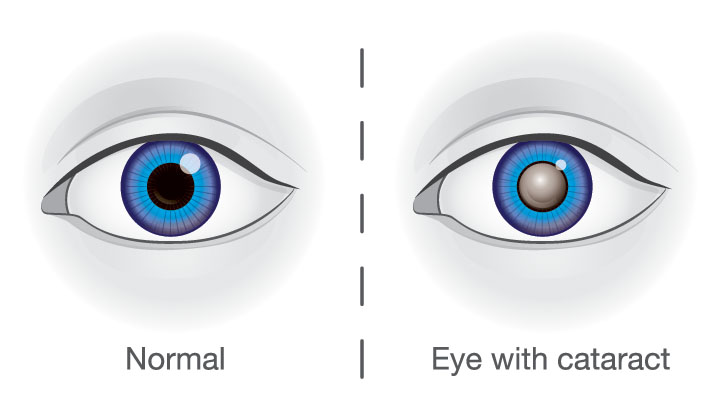
Cataract is a leading cause of blindness and is characterized by the thickening of lenses. Diabetes is a major risk factor for cataracts and causes a condition called diabetic cataract in which transparency of the lens is reduced.
How Diabetes can lead to cataract?
With chronic high blood sugar levels, there are various changes in the eyes. There is reduced oxygen supply, reduced absorption of nutrients and damage to the nerves. As diabetes progresses, fluid starts to accumulate in the lenses of eyes. Stress and pressure caused by this fluid leads to death of cells. This leads to diabetic cataract.
Types of Cataract
- Cataract can occur due to age. This is called senile cataract.
- When cataract occurs in the center of the lens, it is called nuclear cataract.
- Other types of cataract include cortical cataract, and anterior/posterior sub-capsular cataract.
- Cataract can even occur due to trauma or congenital causes.
Diabetic cataract causes stiffening of lenses. It even causes opacity of lenses leading to progressive vision loss. It is one of the leading causes of blindness.
Symptoms of Diabetic Cataract
- Blurry/cloudy vision.
- Glare when looking at bright lights.
- Inability to distinguish between colors.
- Unable to see contrast in colors properly.
- Progressive nearsightedness.
Diabetic Cataract Diagnosis & Treatment
Diabetic cataract is detected using visual acuity test, dilated eye examination, and other tests. It is treated with a cataract surgery and placement of IOL (intraocular lens) implants. First, cataract is extracted. Then, IOL implantation is done.
Once blood sugar levels are controlled, cataract surgery is performed. Surgery is generally keyhole, and takes around 30 to 45 minutes. It is performed under local anesthesia.
Though numerous surgeries of diabetic cataract go without complications, some of them might experience macular edema and infections. This is however very low.
How to Prevent Diabetic Cataract
- Maintain blood sugar levels, and HbA1c at target levels.
- Inform doctor about diabetes before being prescribed with any steroidal medications.
- Wear protective eyeglasses or goggles in order to avoid exposure to UV radiation of the sun.
- Avoid smoking.
- Reduce alcohol consumption.
- Include diet containing omega-3 fatty acids.
- Get frequent dilated eye examinations.