Testing and Monitoring
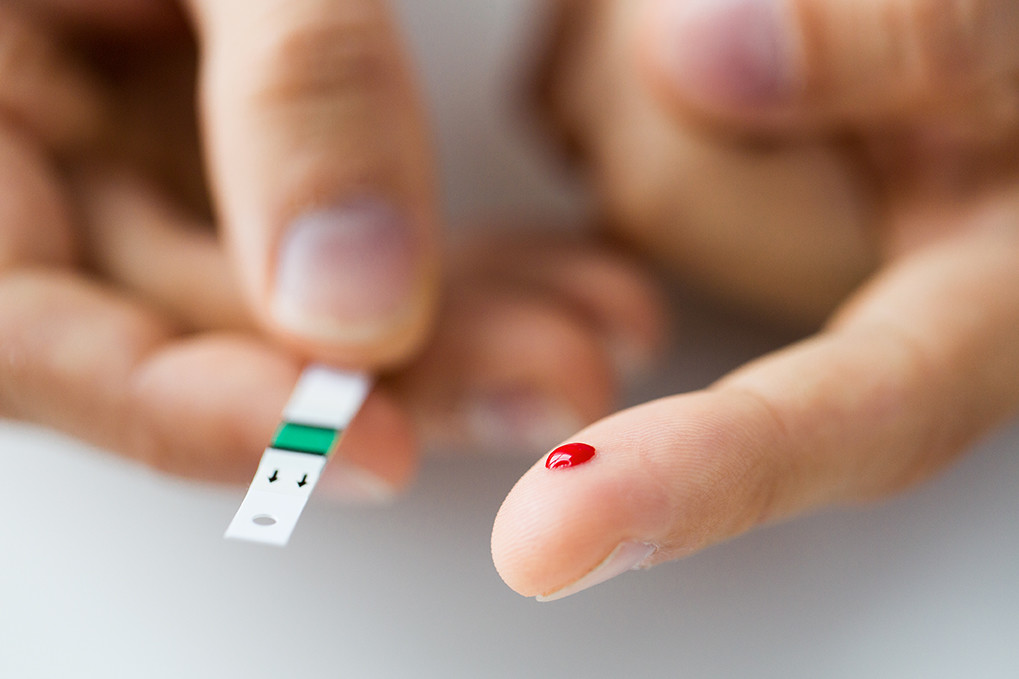
Taking a blood sugar test regularly helps monitor your glucose levels, which is the main aspect when keeping a tab on your diabetes control. Keeping a log of your results is crucial because when your diabetes specialist reviews it, you have a good picture of your body’s response to your diabetes care plan. Let’s know more about how you can successfully test and monitor your diabetes.
Blood sugar test:
Self-monitoring for diabetes
Your diabetes specialist will suggest the frequency of your blood sugar test depending on the ongoing type of treatment, current glucose control in terms of HbA1c (glycated hemoglobin), which determines what your average blood sugar levels are), and the treatment goals established. Accordingly, you can follow the plan so as to avoid consequences of low and high sugar level. Take a blood sugar test anytime using a device called glucometer.
Other recommended tests or examinations
As people with diabetes have a high risk of developing serious complications, in addition to blood sugar test, they’re also recommended:
A visit every 3-6 months to review:
- HbA1c (Every 3 months if on insulin / Every 6 months if on oral drugs)
- Diet and physical activity review
- Blood pressure
- Weight and BMI
- Feet, if positive for neuropathy
- If smoking has been stopped
A visit annually to check:
Diabetic Nephropathy Tests:
- Urine Albumin (type 1 diabetes: duration ≥5yrs / type 2 diabetes: at diagnosis and thereafter)
- Serum creatinine with estimated GFR (kidney test), Potassium
Diabetic Retinopathy Tests:
Comprehensive eye examination by ophthalmologist or optometrist. If not positive for retinopathy, should be examined every year.
Distal Symmetric Neuropathy
(type 1 diabetes: duration ≥5yrs / type 2 diabetes: at diagnosis and thereafter)
- Foot examination.
- Risk factors for ulcer, inspection, assessment of foot pulses, and testing for loss of sensation.
Aside from the above steps to monitor and keep a check on diabetes from advancing, people at risk of diabetes (with family history, sustained poor lifestyle habits), can keep a check on their blood glucose levels and risk of developing diabetes through:
- Non invasive diabetes risk assessment which gives a sense of one’s chances of developing diabetes.
- Glucose Tolerance Test – used to test for diabetes and more exact since it involves a blood test.